Experiencing a head injury, especially in a car accident, can be a frightening event. While minor bumps might cause temporary discomfort, more severe impacts can lead to serious complications. Diagnostic tools like a head CT scan play a crucial role in evaluating the extent of the damage. A common concern after such incidents is whether a CT scan is necessary. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of head injuries, their symptoms, and the guidelines for determining when a CT scan is needed, particularly in the context of car accidents.
Understanding Head Injuries from Car Accidents
To determine the necessity of a CT scan, it’s essential to first understand what constitutes a head injury. In simple terms, a head injury encompasses any trauma to the scalp, skull, or brain. This can range from minor bruises and cuts to fractures and internal brain damage. Car accidents are a significant cause of head injuries due to the sudden deceleration and potential impact within the vehicle or with external objects.
Head injuries are broadly classified into two categories: closed and open. A closed head injury occurs when the skull remains intact, even with internal damage to the brain. Conversely, an open head injury involves a skull fracture, increasing the risk of infection and direct brain exposure. Closed head injuries are more frequently observed in car accidents.
Alt text: Infographic explaining concussion symptoms, including headache, nausea, dizziness, and balance problems, relevant to head injuries from car accidents.
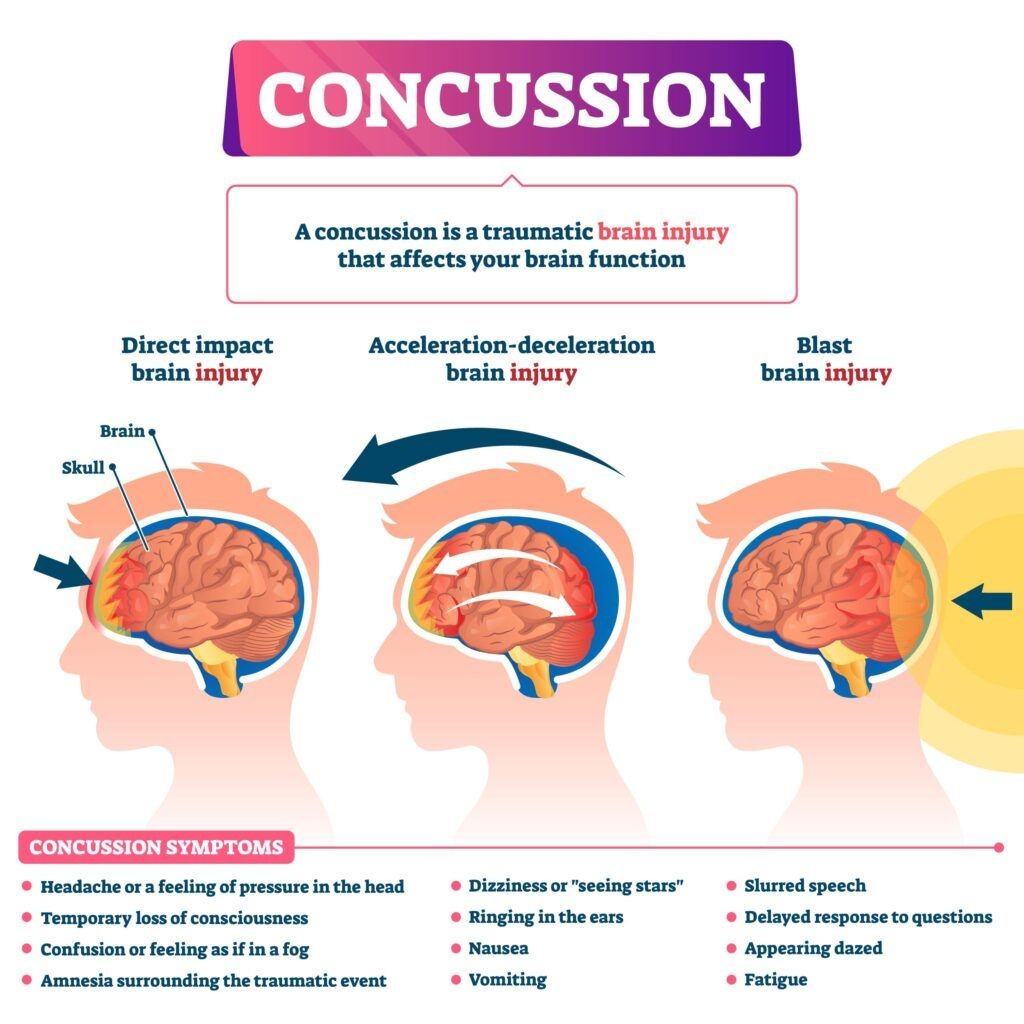
Within closed head injuries, concussions are prevalent, particularly in car accidents. A concussion is a mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) resulting from the head being jolted or struck. The force causes the brain to move within the skull, potentially leading to bruising, bleeding, and nerve cell damage. Symptoms of a concussion can vary, but common indicators include:
- Headache
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Dizziness or Vertigo
- Blurred Vision
- Sensitivity to Light (Photophobia)
- Sensitivity to Noise (Phonophobia)
- Balance Issues
- Fatigue or Drowsiness
- Difficulty Concentrating or Memory Problems
Beyond concussions, car accidents can result in more severe types of head injuries that may necessitate a CT scan for accurate diagnosis:
Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI)
DAI is a serious brain injury often caused by the violent shaking or rotational forces experienced in car accidents. This type of injury damages the axons, the nerve fibers that transmit signals throughout the brain, leading to widespread brain dysfunction.
Cerebral Edema
Edema refers to swelling of the brain tissue. Following a head injury in a car accident, the brain may swell in response to trauma. This swelling can increase pressure within the skull, potentially causing further brain damage.
Hematoma
A hematoma is a collection of blood outside blood vessels. In the context of head injuries from car accidents, hematomas can form within the brain tissue (intracerebral hematoma) or between the skull and brain (epidural or subdural hematoma). These blood collections can compress brain tissue and require prompt medical attention.
Hemorrhage
Hemorrhage signifies bleeding. Intracerebral hemorrhage refers to bleeding within the brain tissue itself, while subarachnoid hemorrhage involves bleeding in the space surrounding the brain. Both types of hemorrhages are serious complications of head injuries sustained in car accidents.
Skull Fracture
A skull fracture, a break in one or more skull bones, is a significant concern after a car accident. While not always directly indicative of brain damage, a skull fracture increases the likelihood of brain injury and may require a CT scan to assess underlying damage.
Determining the Need for a CT Scan After a Car Accident
After a car accident involving a head injury, seeking medical evaluation is paramount, regardless of the perceived severity. If you experience any of the concussion symptoms mentioned earlier, medical attention is crucial. These symptoms can indicate not only a concussion but also more serious underlying brain injuries. Immediate emergency care is vital if there is loss of consciousness, confusion, or disorientation following a car accident. A medical professional can properly assess the head injury and determine if a CT scan is necessary.
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, is an advanced imaging technique utilizing X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body, including the brain. In the context of head injuries, particularly after car accidents, a CT scan is invaluable for visualizing the brain and skull. It allows doctors to detect critical issues such as bleeding, swelling, and skull fractures that may not be apparent through physical examination alone.
Alt text: Medical professional performing a head CT scan on a patient, a common diagnostic procedure after car accident head injuries.
Generally, a routine CT scan is not recommended for every individual who experiences a minor head injury, such as a simple concussion, after a car accident. Many mild traumatic brain injuries do not present with findings detectable on a CT scan, and these injuries often resolve with conservative management. Moreover, CT scans expose patients to radiation, and therefore are judiciously used when the clinical benefit outweighs the risk.
However, specific signs and risk factors elevate the necessity for a CT scan following a car accident head injury. A CT scan is typically indicated in situations where there is a concern for more severe brain injury. These include:
- Speech, Hearing, or Swallowing Difficulties: New onset problems in these areas after a car accident head injury can signify neurological damage requiring investigation with a CT scan.
- Seizures: Post-traumatic seizures are a serious sign of brain injury and warrant immediate CT scanning to identify underlying causes.
- Vision Problems: Changes in vision after a head injury, such as double vision or loss of vision, may indicate brain trauma requiring a CT scan.
- Weakness on One Side of the Face or Body: Unilateral weakness is a neurological red flag suggesting potential brain injury that needs to be evaluated with a CT scan.
- Prolonged Loss of Consciousness: Any extended period of unconsciousness after a car accident head injury necessitates a CT scan to rule out serious brain damage.
- Unequal Pupil Size (Anisocoria): Mismatched pupil sizes can indicate increased pressure within the skull and is a strong indicator for a CT scan.
- Skull Tenderness: Significant tenderness upon palpation of the skull after a car accident can suggest a fracture, prompting the need for a CT scan.
- Severe Vomiting and/or Headache: Persistent, severe vomiting or worsening headache after a head injury, especially in conjunction with other symptoms, may warrant a CT scan.
- Fluid Leakage from Ear or Nose: Clear or bloody fluid discharge from the ears or nose after a head injury can be a sign of a skull fracture and cerebrospinal fluid leak, necessitating a CT scan.
Furthermore, individuals with certain risk factors are more likely to undergo a CT scan after a car accident head injury, even with less severe symptoms. This includes individuals on blood-thinning medications, elderly individuals, and those with pre-existing neurological conditions.
Conclusion: When to Consider a CT Scan After a Car Accident Head Injury
In summary, while not every head injury sustained in a car accident requires a CT scan, it is crucial to be aware of the signs and symptoms that warrant immediate medical attention and potential CT imaging. If you or someone you know experiences a head injury in a car accident, especially with concerning symptoms or risk factors, prompt medical evaluation is essential. A healthcare professional can accurately assess the situation and determine if a CT scan is necessary to rule out serious brain injuries and guide appropriate management. Prioritizing medical assessment after a car accident head injury is always the safest course of action.
Alt text: Headshot of Dr. Kashouty, a neurologist specializing in neurophysiology, emphasizing the medical expertise related to head injury assessment after car accidents.