Car accidents, even minor ones, can be jarring and lead to a range of injuries. Among the most common complaints after a car accident is a headache. While some headaches may be benign and resolve on their own, others could indicate a more serious underlying issue, particularly a head injury. This naturally leads to the question: is a CT scan good for a headache after a car accident? This article will explore when a CT scan might be necessary after a car accident-related headache, helping you understand the types of head injuries, associated symptoms, and guidelines for seeking appropriate medical evaluation.
Understanding Head Injuries from Car Accidents
A head injury from a car accident can range from a minor bump to severe trauma. In medical terms, a head injury encompasses any damage to the brain, skull, or scalp caused by an external force. Car accidents are a frequent cause of these injuries, often due to sudden stops, impacts, and rapid changes in motion.
Head injuries are broadly classified into two categories:
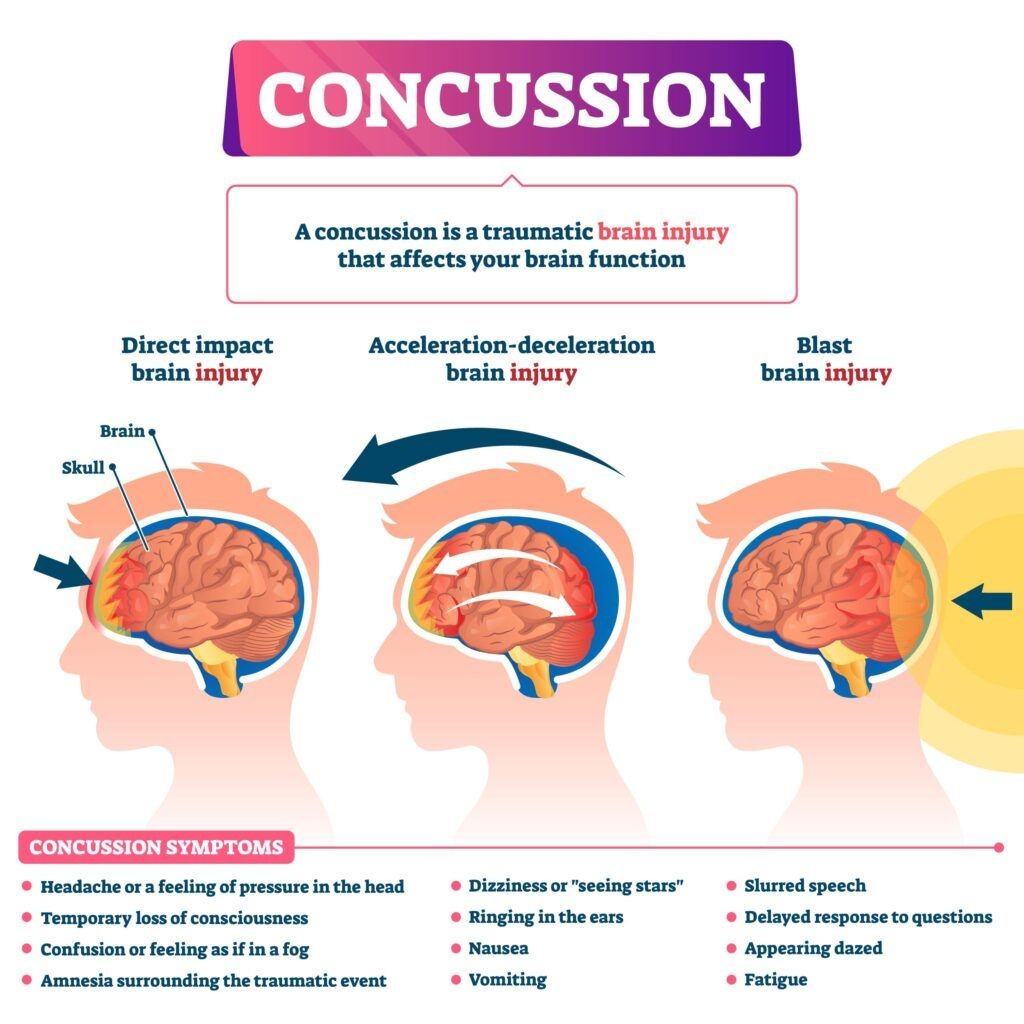
- Closed Head Injury: This occurs when the skull remains intact, even with internal brain damage. These are more common in car accidents and can result from the brain hitting the inside of the skull. Concussions are the most prevalent type of closed head injury.
- Open Head Injury: This involves a fracture in the skull, exposing the brain to potential external damage. While less common than closed head injuries, they are more serious and often require immediate and intensive medical intervention.
The force of a car accident can cause various types of brain injuries, including:
-
Concussion: A mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head that causes the brain to move rapidly inside the skull. This can lead to temporary neurological dysfunction. Symptoms of a concussion after a car accident can include:
- Headache
- Nausea and Vomiting
- Dizziness or Balance Issues
- Blurred Vision
- Sensitivity to Light and Noise
- Fatigue or Drowsiness
- Difficulty Concentrating or Memory Problems
-
Diffuse Axonal Injury (DAI): This more severe injury is caused by the brain rapidly shifting inside the skull, often from sudden acceleration and deceleration in car accidents. DAI causes widespread damage to brain cells.
-
Edema (Swelling): Brain swelling in response to injury, increasing pressure inside the skull.
-
Hematoma: A collection of blood outside blood vessels. In the context of head injuries, hematomas can occur in the scalp or within the brain, leading to increased pressure and potential brain damage.
-
Hemorrhage (Bleeding): Bleeding can occur within the brain tissue (intracerebral hemorrhage) or around the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage), both serious conditions requiring prompt medical attention.
-
Skull Fracture: A break in one or more skull bones, indicating a higher risk of brain damage.
Headaches After Car Accidents: When to Worry?
Experiencing a headache after a car accident is not uncommon. However, the nature and severity of the headache, along with other accompanying symptoms, are critical in determining the need for further investigation, such as a CT scan.
While a simple headache might be due to muscle tension or stress from the accident, it can also be a primary symptom of a concussion or a more serious head injury. It’s important to be vigilant and seek medical advice if you experience a headache along with any of the following symptoms after a car accident:
- Severe Headache: A sudden, intense headache that is significantly worse than typical headaches.
- Persistent Headache: A headache that doesn’t improve or worsens over time.
- Headache with Concussion Symptoms: Any of the concussion symptoms listed above (nausea, vomiting, dizziness, vision problems, etc.) accompanying a headache.
- Loss of Consciousness: Even a brief loss of consciousness after the accident warrants immediate medical evaluation.
- Confusion or Disorientation: Feeling confused, having difficulty remembering the accident, or being disoriented.
- Neurological Deficits: Weakness, numbness, or tingling on one side of the body, difficulty speaking, or vision changes.
- Seizures: Any seizure activity post-accident is a serious sign.
- Fluid Leakage: Clear or bloody fluid draining from the ears or nose can indicate a skull fracture.
- Pupil Size Mismatch: Unequal pupil sizes can be a sign of increased pressure within the skull.
CT Scans: When Are They Necessary After a Car Accident Headache?
A CT scan, or Computed Tomography scan, is a powerful diagnostic tool that uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body, including the brain. In the context of head injuries, a CT scan is invaluable for visualizing the skull and brain to detect fractures, bleeding, swelling, and other abnormalities.
While CT scans are highly effective in diagnosing significant head injuries, they are not routinely recommended for everyone who experiences a headache after a car accident. This is because:
- Radiation Exposure: CT scans use ionizing radiation. While the risk from a single scan is low, it’s important to limit radiation exposure when not medically necessary, especially for mild injuries.
- Concussions Often Don’t Show on CT Scans: Mild traumatic brain injuries like concussions may not always be visible on a standard CT scan. CT scans are better at detecting structural damage like fractures and bleeds, rather than the subtle cellular and functional changes associated with concussions.
However, a CT scan is typically recommended after a car accident-related headache if there are “red flag” symptoms or risk factors present. These include:
- Presence of any symptoms mentioned in the “When to Worry” section: Severe headache, persistent headache with concussion symptoms, loss of consciousness, confusion, neurological deficits, seizures, fluid leakage, or pupil size mismatch.
- High-Risk Factors:
- Age over 65: Older adults are at higher risk for complications from head injuries.
- Anticoagulant Use (Blood Thinners): Increased risk of bleeding.
- Significant Mechanism of Injury: High-speed collisions, rollovers, or accidents with significant vehicle damage.
- History of Bleeding Disorders.
- Intoxication: Altered mental status due to alcohol or drugs can mask symptoms and make clinical assessment difficult.
In these situations, a CT scan helps to quickly rule out serious conditions like skull fractures, brain hemorrhages, or significant brain swelling that require immediate medical or surgical intervention.
Seeking Medical Attention is Key
If you experience a headache after a car accident, it’s always prudent to seek medical evaluation. While not every headache necessitates a CT scan, a healthcare professional can properly assess your symptoms, medical history, and the details of the accident to determine the appropriate course of action.
Do not hesitate to seek immediate medical attention, especially at the emergency room, if you experience any of the “red flag” symptoms mentioned above, or if you are concerned about your headache after a car accident. A medical professional will conduct a neurological examination and decide if a CT scan or other diagnostic tests are necessary to ensure your well-being.
In Conclusion
Experiencing a headache after a car accident is a common concern. While a CT scan is a valuable tool for diagnosing serious head injuries, it’s not automatically required for every post-accident headache. The decision to perform a CT scan is based on a careful assessment of your symptoms, risk factors, and the nature of the accident. The most important step is to seek timely medical attention after a car accident if you develop a headache, especially if it is accompanied by concerning symptoms. Prompt medical evaluation will ensure that you receive the appropriate diagnosis and care, prioritizing your health and recovery.