In the realm of Wi-Fi security, the concept of a hidden SSID (Service Set Identifier) is often misunderstood. The idea behind hiding your Wi-Fi network name is to add a layer of obscurity, making it less visible to casual onlookers. However, as a security measure, hiding your SSID is largely considered ineffective and more of an outdated practice. This article will delve into the mechanics of hidden SSIDs and, more importantly, guide you on how to scan for hidden SSIDs to reveal these concealed networks.
While hiding your SSID might seem like a clever way to deter unauthorized access, it’s crucial to understand that it doesn’t truly make your network invisible. Wi-Fi networks, hidden or not, still broadcast signals to function. We’ll explore how these signals can be intercepted and analyzed to uncover the names of hidden networks, effectively debunking the myth of SSID cloaking as robust security.
Understanding Hidden SSIDs and Wi-Fi Broadcasting
To grasp how to scan for hidden SSIDs, we first need to understand how Wi-Fi networks announce their presence. Wireless routers and access points continuously transmit management beacon packets. These packets are like announcements, broadcasting information about the Wi-Fi network so devices in the vicinity can discover and connect to them. This is based on the 802.11 standard that governs Wi-Fi communication.
Think of it like a lighthouse sending out signals. Devices like your smartphone, laptop, and tablet constantly listen for these beacon packets to identify available Wi-Fi networks. This is why you see a list of Wi-Fi networks when you try to connect. Your devices are picking up these broadcasted announcements.
Alt Text: A packet capture showing a Wi-Fi management beacon frame, highlighting the area where the hidden SSID would typically be displayed but is intentionally left blank.
When a Wi-Fi network is set to broadcast its SSID (the default setting), the beacon packets contain the network’s name. Devices receive these packets and display the network name in the list of available Wi-Fi connections. This user-friendly system allows for easy network discovery and connection.
The Illusion of Invisibility: How Hidden SSIDs Work (and Don’t Work)
When a network administrator chooses to hide the SSID, they are essentially configuring the access point to omit the network name from the management beacon packets. The network is still broadcasting, but it’s doing so without openly declaring its name in every beacon.
To connect to a hidden SSID, you can’t simply choose it from a list. You must manually enter the network name, along with the password, if required. This is the primary difference in the connection process and the basis of the perceived “security” of hidden SSIDs.
Alt Text: Comparison of two Wi-Fi management beacon packets: one showing a standard network broadcasting its SSID, and the other demonstrating a hidden SSID where the network name is absent from the beacon frame.
However, the crucial point is that hiding the SSID only prevents passive discovery. It doesn’t stop devices from actively probing for networks or reveal the SSID during the connection process itself. This is where the weakness of hidden SSIDs and the methods to scan for them come into play.
Why Hidden SSIDs Aren’t Truly Hidden: Active Probing and Network Analysis
While access points with hidden SSIDs don’t announce their names in beacon packets, client devices (like your phone or laptop) often give away the hidden SSID when they attempt to connect.
Here’s how: When a device has previously connected to a hidden network, it will periodically send out “probe request” packets. These packets are essentially the device asking, “Is network ‘X’ (the hidden SSID) around?”. These probe requests do contain the hidden SSID, as the device needs to identify the specific network it wants to rejoin.
Anyone with the right tools can “listen” to these wireless signals. By capturing and analyzing these probe request packets, the hidden SSID is revealed. This is the fundamental principle behind scanning for hidden SSIDs.
Furthermore, even during a normal connection to a hidden SSID, the network name is transmitted in the clear during the association process. Tools capable of capturing and analyzing Wi-Fi traffic in monitor mode can intercept these packets and extract the hidden SSID.
Tools and Techniques to Scan for Hidden SSIDs
To effectively scan for hidden SSIDs, you need tools that can operate in monitor mode. Monitor mode allows your Wi-Fi adapter to capture all wireless traffic in the air, not just packets directed to or from your device. This is essential for intercepting beacon packets, probe requests, and other management frames that reveal hidden network information.
Wi-Fi Analyzers: Specialized software applications, often called Wi-Fi analyzers or network scanners, are designed for this purpose. These tools leverage monitor mode to capture and analyze wireless traffic, displaying detailed information about nearby networks, including hidden SSIDs.
Acrylic Wi-Fi Analyzer: As mentioned in the original article, Acrylic Wi-Fi Analyzer is a tool specifically designed to detect hidden SSIDs. It utilizes monitor mode to capture network traffic and can identify hidden network names when client devices connect or probe for them. Acrylic Wi-Fi Analyzer, and similar tools, can display the recovered hidden SSID, often highlighting it to distinguish it from openly broadcasted networks.
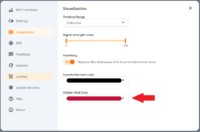 Display hidden SSID network name
Display hidden SSID network name
Alt Text: Screenshot of a Wi-Fi analyzer interface, showcasing a list of detected networks, with a hidden SSID clearly identified and displayed in color after being successfully revealed by the software.
Other Wi-Fi Scanning Tools: Besides Acrylic Wi-Fi Analyzer, various other tools are available, such as Kismet, Wireshark (with appropriate plugins), and command-line tools like airodump-ng (part of the Aircrack-ng suite). These tools, when used with a compatible Wi-Fi adapter in monitor mode, can also effectively scan for and reveal hidden SSIDs.
Step-by-Step Process to Scan for Hidden SSIDs (Using a Wi-Fi Analyzer)
While the specific steps may vary slightly depending on the Wi-Fi analyzer tool you choose, the general process for scanning hidden SSIDs is as follows:
-
Enable Monitor Mode: Ensure your Wi-Fi adapter is capable of and configured for monitor mode. This often involves using specific drivers or commands depending on your operating system and Wi-Fi adapter.
-
Launch Wi-Fi Analyzer: Start your chosen Wi-Fi analyzer application.
-
Start Network Capture: Initiate the network capture or scanning process within the Wi-Fi analyzer. The tool will begin listening for wireless traffic in your vicinity.
-
Observe Network List: The Wi-Fi analyzer will display a list of detected Wi-Fi networks. Initially, hidden SSIDs might appear as “[Hidden Network]” or similar generic names.
-
Wait for SSID Reveal: As devices in the area interact with the hidden network (e.g., a device connects to it or sends probe requests), the Wi-Fi analyzer will capture the relevant packets. It will then analyze this data to identify and display the actual hidden SSID name. This process might take a few moments or longer depending on network activity.
-
Identify the Hidden SSID: Once the hidden SSID is revealed, it will be displayed in the Wi-Fi analyzer interface, often highlighted or clearly labeled.
Conclusion: Hidden SSIDs – Obscurity, Not Security
As we’ve demonstrated, scanning for hidden SSIDs is not a complex task with the right tools. The practice of hiding your SSID provides a minimal level of obscurity but offers virtually no real security against determined individuals. It’s akin to hiding your house key under the doormat – it might deter casual passersby, but it won’t stop someone who is actually trying to get in.
For robust Wi-Fi security, focus on strong encryption (WPA3 is recommended), strong passwords, access control, and keeping your router firmware updated. Understanding how to scan for hidden SSIDs highlights the importance of moving beyond outdated security practices and adopting more effective measures to protect your wireless network.
If you are interested in exploring Wi-Fi network analysis and security further, consider using a Wi-Fi analyzer tool to visualize and understand the wireless landscape around you. It’s a valuable step in becoming more informed about Wi-Fi technology and security best practices.


